Classification
Home > Technology > Classification
Active Noise Control (ANC) Technology Classification I
Single-Channel ANC vs. Multi-Channel ANC
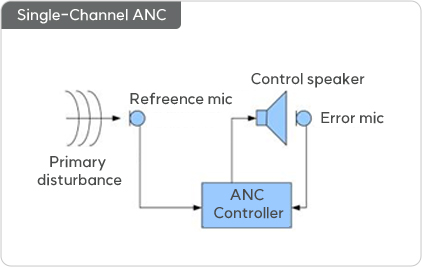
- 01 Single-Channel ANC
- Uses no reference microphone or one reference microphone
- Uses one control speaker
- Uses one error microphone
- 1(0) reference mic x 1 control speaker x 1 error mic
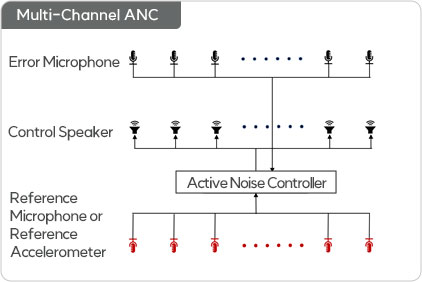
- 02 Multi-Channel ANC
- Uses one or more reference microphones
- Uses one or more control speaks
- Uses one or more error microphones
- J reference mic x K control speaker x M error mic (e.g. 12 x 8 x 8)
Why is Multi-Channel ANC Necessary?
- To overcome a narrow Quiet Zone, Multi-Channel ANC overlaps and expands the Quiet Zone.
Active Noise Control Technology Classification II
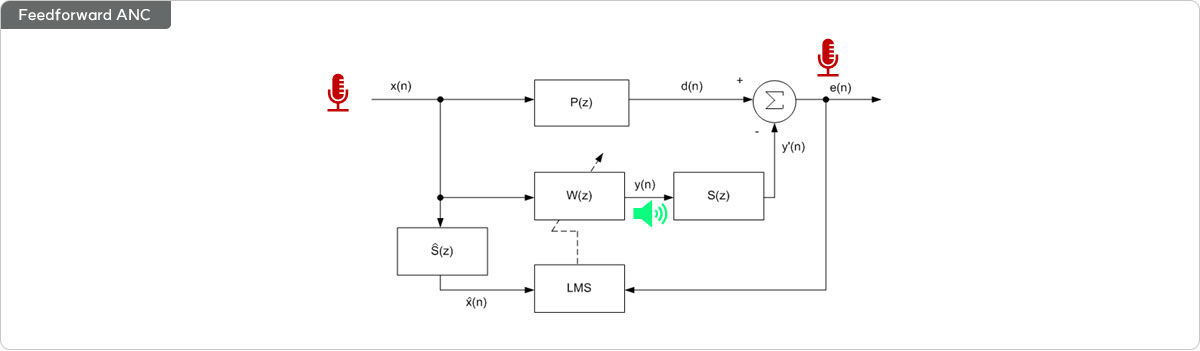
- 01 Feedforward ANC
- Existence of a reference microphone
- Uses a reference microphone signal as prior information to remove random noise
- 02 Block Processing ANC
- Reduces computation through FFT-based Fast Convolution, useful in multi-channel ANC with high computational demands
- Increases output latency and adaptive filter update latency due to block buffering
- Operates on a DMA basis; low interrupt overhead
- Frequency-domain algorithm: Frequency-domain Block FxLMS(FBFxLMS)
- Utilizes the temporal statistical properties of signals obtained through block processing
- Representative algorithms
- Self-Orthogonalized FBFxLMS: Easy calculation of the inverse of Diagonalized Autocorrelation Matrix
- Subband FxLMS: Filter-bank based algorithm; computation reduction through Decimation
- 03 Hybrid Processing ANC
- For the output of ANC controller, sample-processed in Time-domain
- For the adaptive filter update of the controller, block-processed in Frequency-domain
- No output latency, but there is adaptive filter update latency
- Disadvantageous when the noise characteristics change rapidly over time
- Utilizes the temporal statistical properties of signals obtained through block processing
- Representative algorithms
- Time-Frequency FxLMS (Delayless Frequency-domain FxLMS)
- Delayless Subband FxLMS

